Medical Library
Pick a Body Area
BPPV and Physical Therapy
Epley Maneuver is Helpful for Vertigo
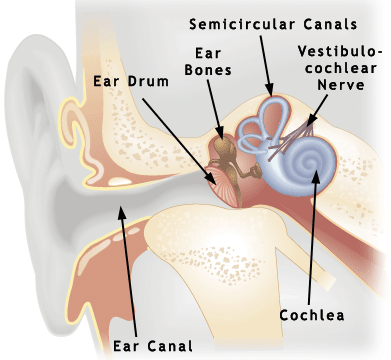
Vertigo, in particular "benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV)", is a common disorder in which the patient complains of spinning and dizziness with rapid changes in head positions. BPPV is typically idiopathic (of unknown cause) in nature. Other reported causes are head trauma, vestibular neuritis (inflamed vestibulo-cochlear nerve), vertebrobasilar ischemia (inadequate blood flow to the brain), and inner ear infection.
It is hypothesized that small particles, (called otoconia) in the semi-circular canals, over-stimulate the sense organs (hair cells and cupula). This results in patient complaints of dizziness and the observation of nystagmus in the direction of head rotation. The dizziness may last anywhere from a few seconds to a minute and there may be associated nausea.
Brandt-Daroff and canalith repositioning movements (Epley Maneuver) are the most common therapeutic interventions. The goal of these treatments is to move the small particles within the semicircular canal to the utricle where they no longer are able to stimulate the sense organs within the canal.
Hi-quality research studies show significant numbers of patients that experience a resolution of symptoms and negative diagnostic tests for BPPV after treatment intervention as compared to the control groups.
While BPPV is a common diagnosis for those suffering from dizziness, there are other causes of vertigo (both central and peripheral). It is important to consult your doctor and physical therapist regarding proper diagnosis and treatment of vertigo.
Disclaimer
The information in this medical library is intended for informational and educational purposes only and in no way should be taken to be the provision or practice of physical therapy, medical, or professional healthcare advice or services. The information should not be considered complete or exhaustive and should not be used for diagnostic or treatment purposes without first consulting with your physical therapist, occupational therapist, physician or other healthcare provider. The owners of this website accept no responsibility for the misuse of information contained within this website.
