OVERVIEW
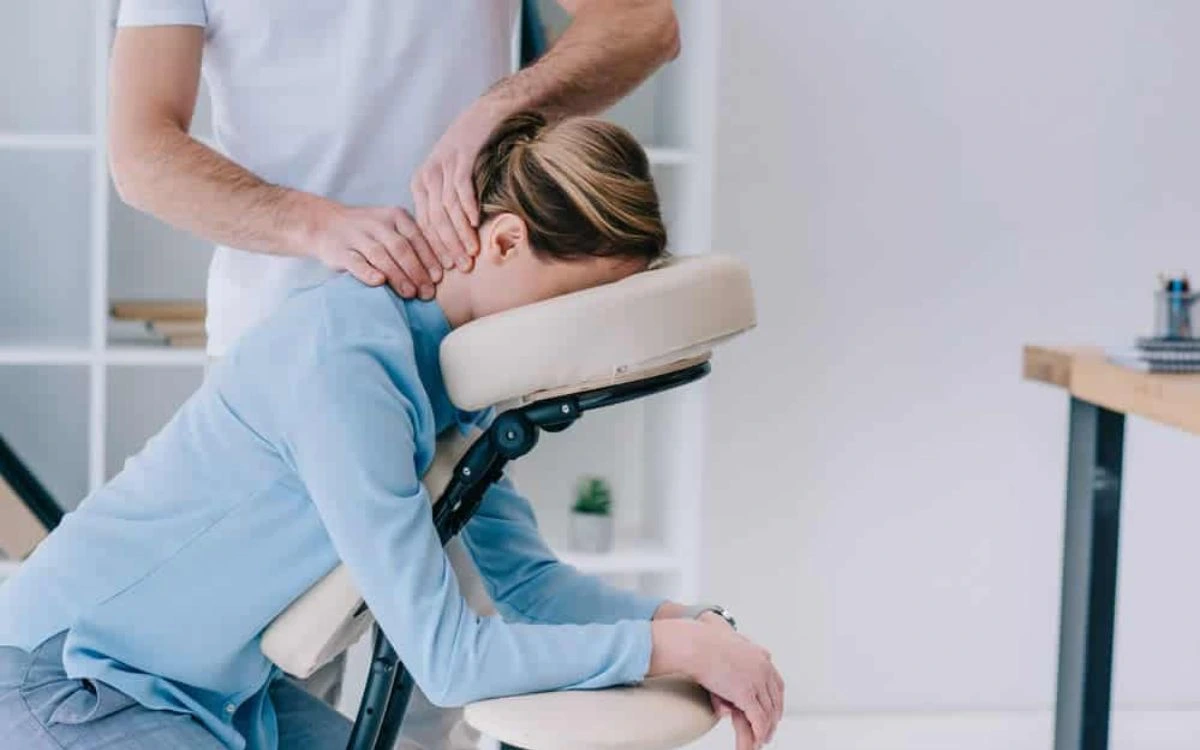
Whiplash (or Whiplash Associated Disorder) – Whiplash is the term for the sudden forward or backward movement of the neck and head, most often occurring in a motor vehicle accident. You may also experience whiplash during other activities, such as competitive and recreational sports. A whiplash can also be caused by a sudden side-to-side motion.
Consumers and the insurance industry will be paying billions each year for WADs. A WAD can cause soft tissue injury, fractures of bones, and nerve damage. Recovery can take several months to complete due to the many structures involved (bone, spine, brain, nerve, ligament, intervertebral disk, muscle, joint capsule and tendon). Most whiplash cases resolve within a few months.
The Quebec Task Force, a group that conducted extensive research on Whiplash, offered a classification of WAD:
- 0 – No complaints or physical signs about the neck.
- 1 – Neck pains, stiffness or tenderness.
- 2 – Neck complaint and Musculoskeletal signs (decreased range motion and tenderness at the point)
- 3 – Neck complaint and neurological signs (decreased, absent deep tendon reflexes or weakness, sensory deficits, and/or sensory deficits).
- 4 – Neck complaints and fracture or dislocation
Your physician may order X-rays or other diagnostics to rule out fractures.
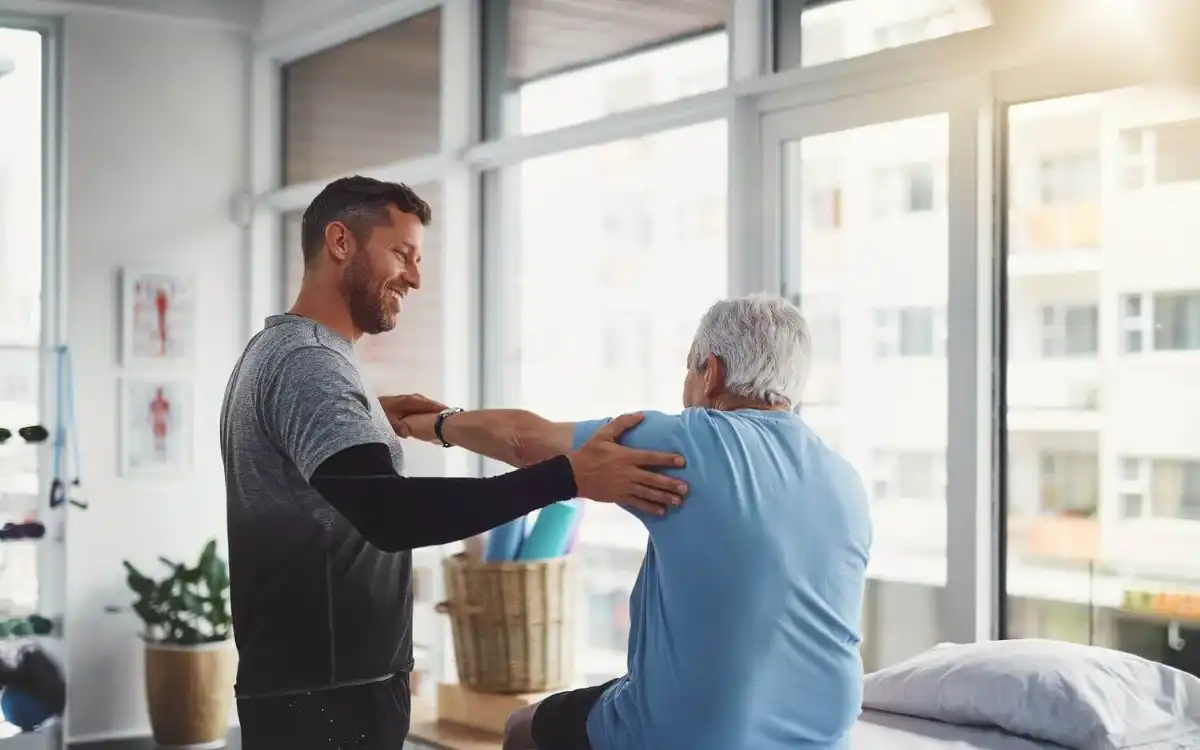
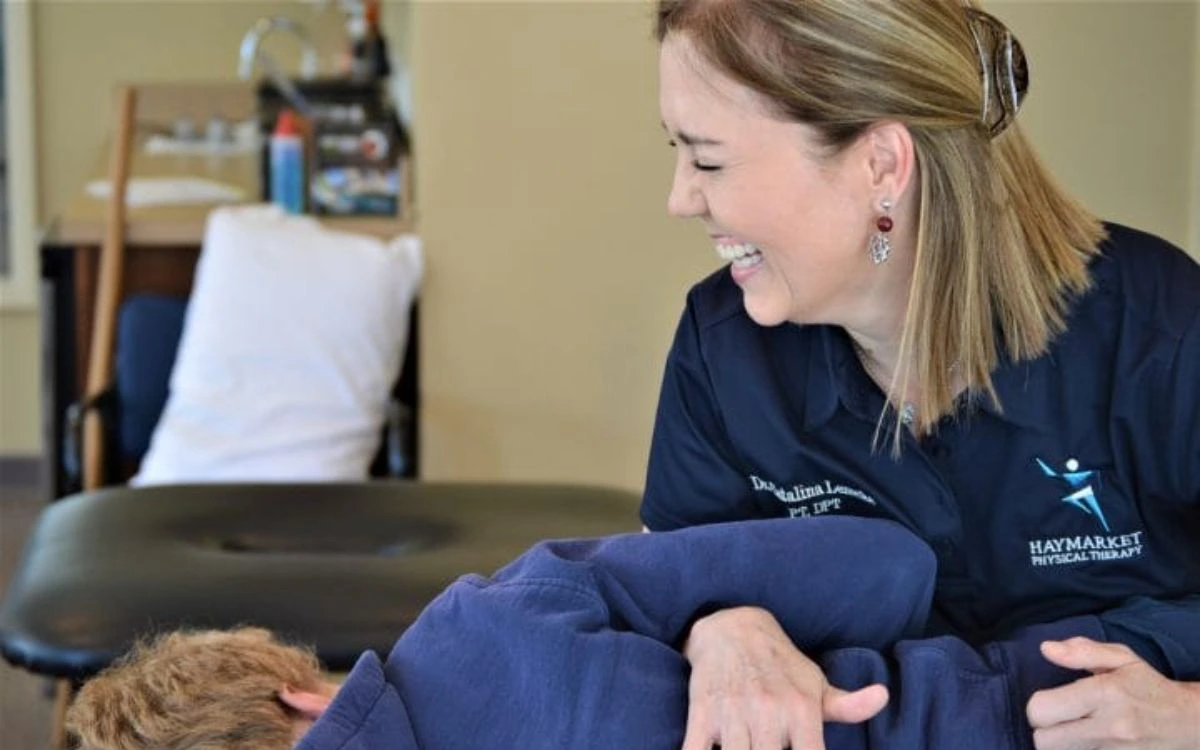
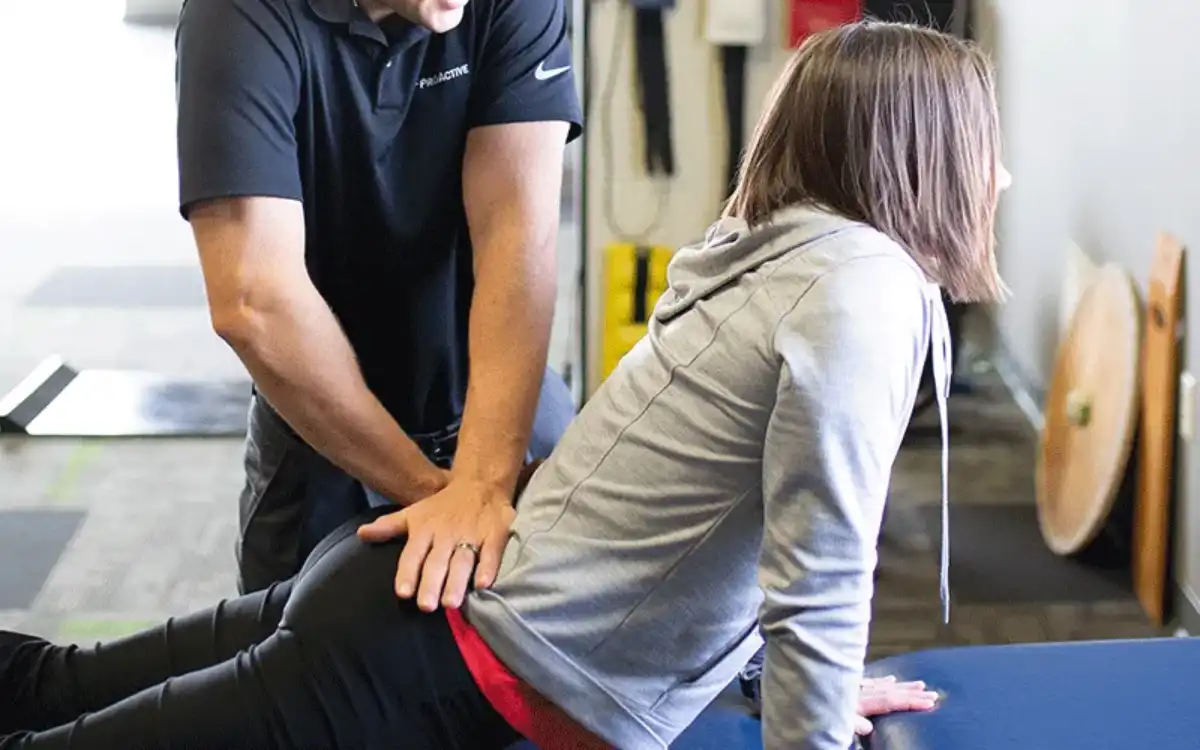
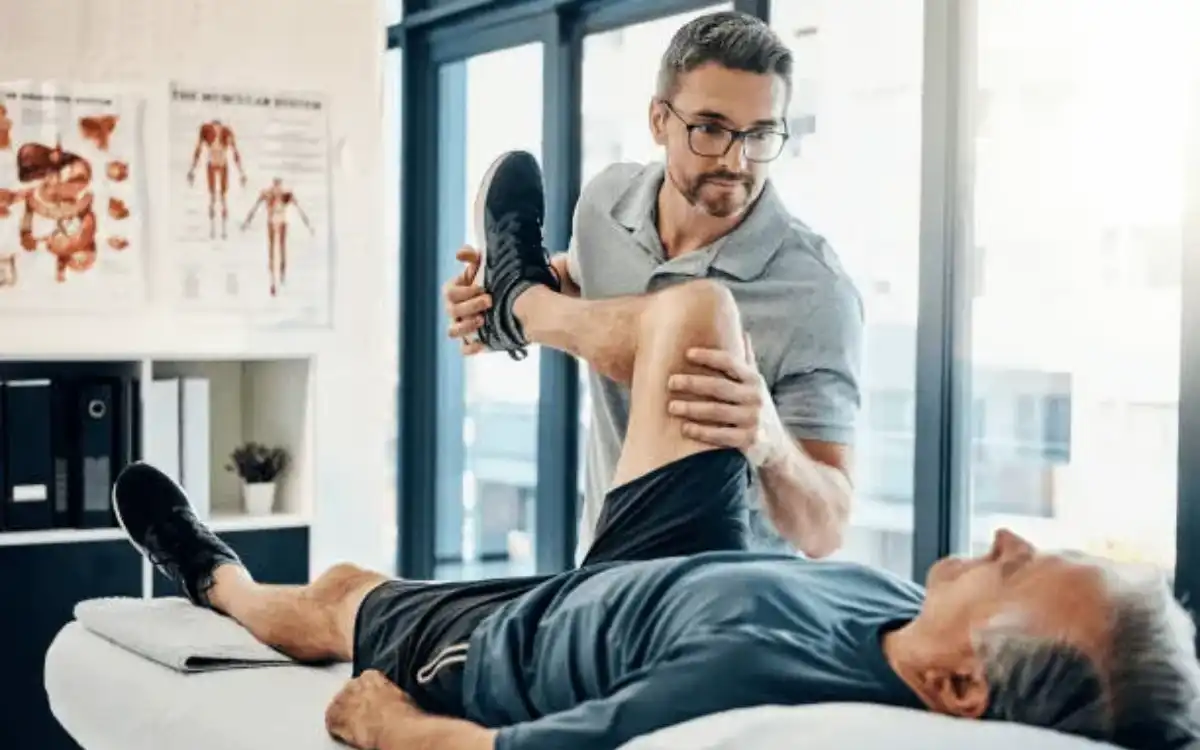
Physical therapy can be extremely helpful in the management of pain, strength, endurance and range of motion. While soft collars can be of limited benefit, rigid collars may prove to be beneficial in the early stages of recovery.
TREATMENT
Possible Treatments
- Aerobic/Endurance Exercise
- Core Strengthening
- Cryotherapy or Cold Therapy
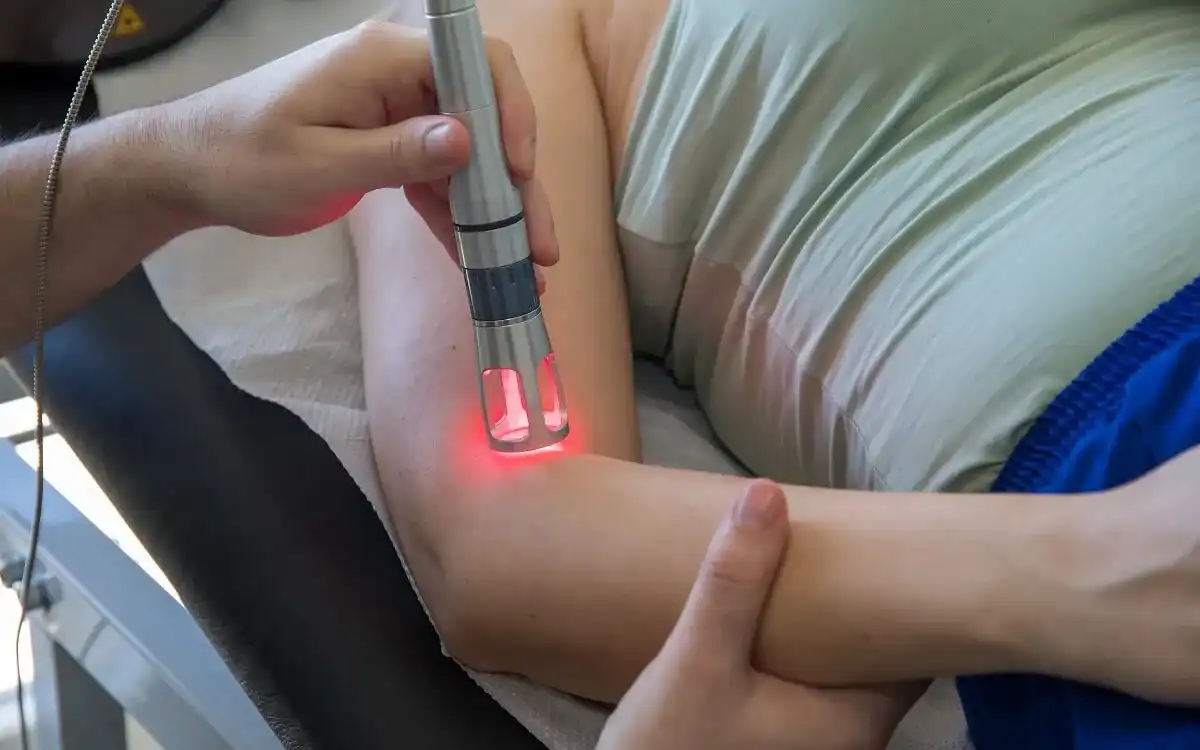
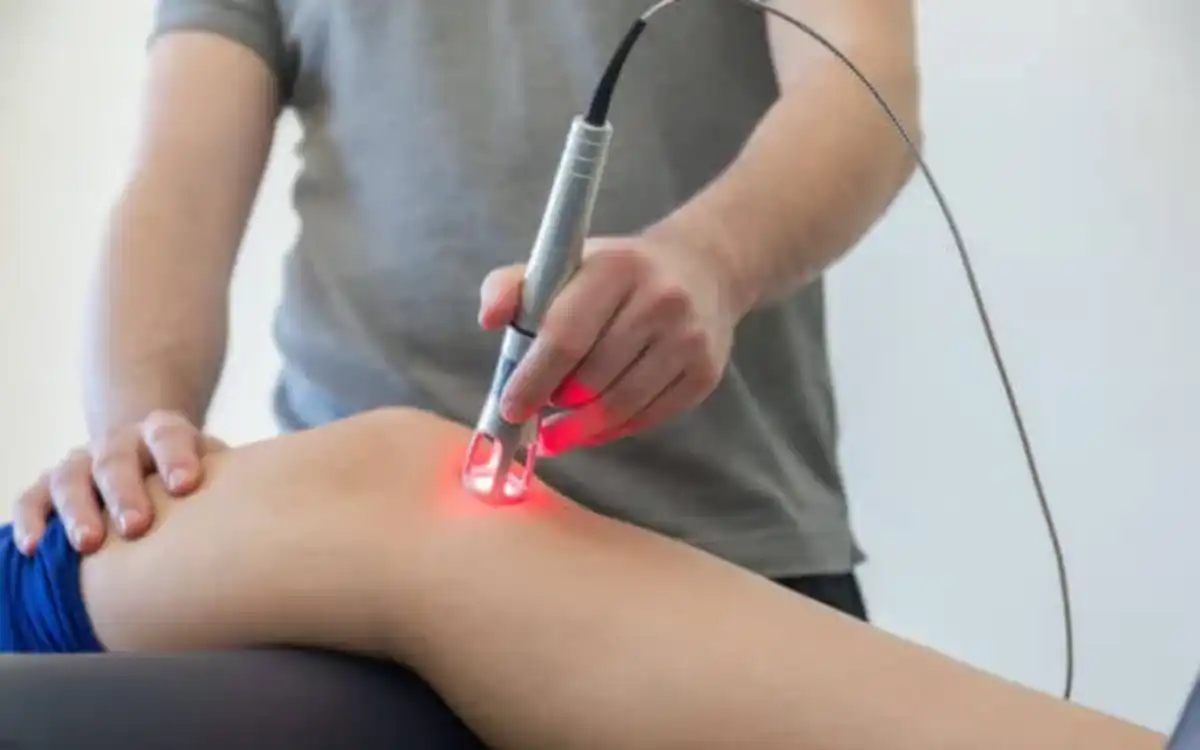
- Electrotherapeutic Modalities
- Heat Pack
- Isometric Exercise
- Neck Active Range of Motion
- Neck Joint Mobilization
- Neck Passive Range of Motion
- Neck Resistive Range of Motion
- Neck Traction
- Posture Training
- Proprioception Exercises
- Physical Agents
- Soft Tissue Mobilization
- Stretching/Flexibility Exercise