OVERVIEW
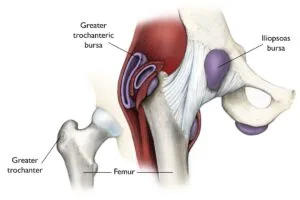
Trochanteric Bursitis
Bursas are fluid-filled bags that reduce shear forces between the tissues of the body. Trochanteric Bursitis, also known as inflammation of a bursa, is caused by excess stress on the bursa that connects the IT Band to the greater trochanter. The symptoms of trochanteric bursitis include pain around the outer hipbone. This can be exacerbated by excessive walking, standing on the affected side or lying on the affected side. The treatment options include rest, ice and compression, as well as physical therapy, stretching, progressive strengthening and steroid injections.
TREATMENT
Possible Treatments
- Aerobic/Endurance Exercise
- Core Strengthening
- Cryotherapy or Cold Therapy
- Electrotherapeutic Modalities
- Gait or Walking Training
- Hip Active Range of Motion
- Hip Joint Mobilization
- Hip Passive Range of Motion
- Hip Resistive Range of Motion
- Isometric Exercise
- Iontophoresis
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF)
- Proprioception Exercises
- Physical Agents
- Soft Tissue Mobilization
- Stretching/Flexibility Exercise
GOALS
Possible Treatment Goals
- Improve Balance
- Decrease Risk of Reoccurrence
- Improve Fitness
- Improve Function
- Improve Muscle Strength and Power
- Increase Oxygen to Tissues
- Improve Proprioception
- Improve Range of Motion
- Self-care of Symptoms
- Improve Tolerance for Prolonged Activities