OVERVIEW
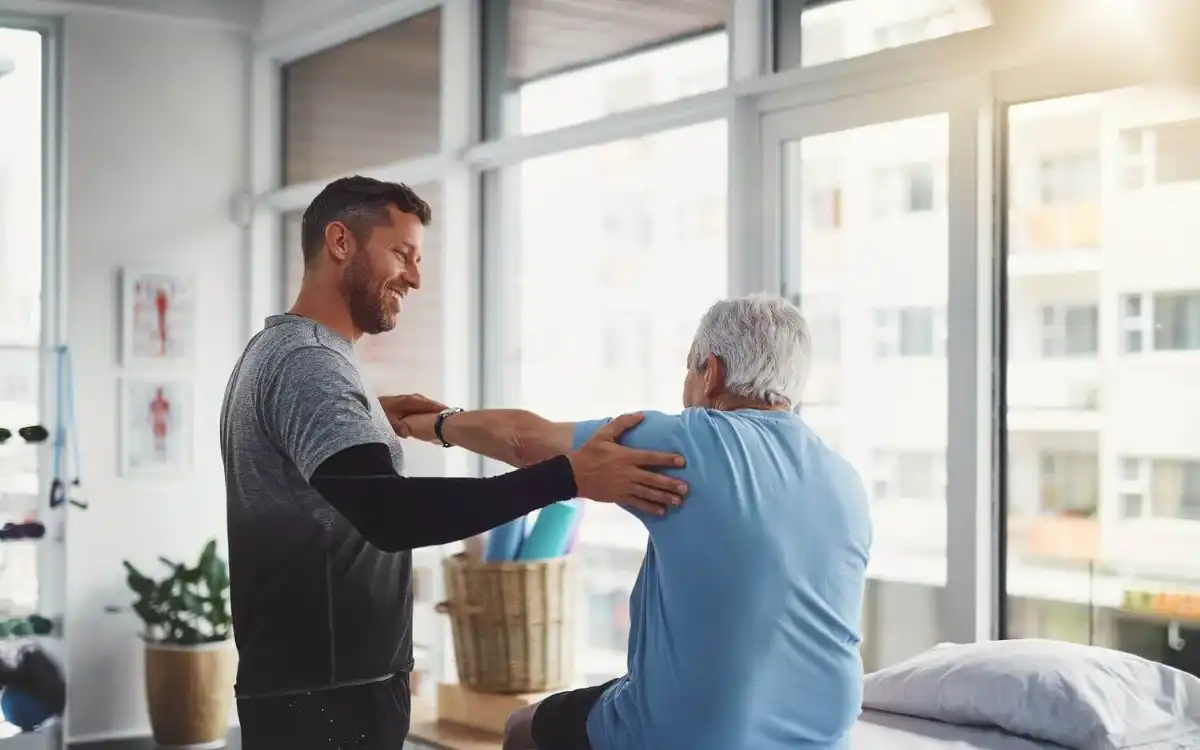
Rotator Cuff Tears
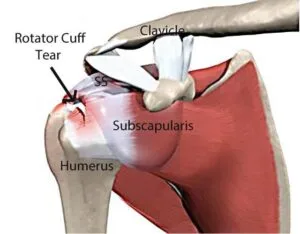
When a young person experiences trauma, such as a fall, rotator cuff tears can occur. Rotator cuff tears can also occur in seniors and middle-aged individuals. This is usually due to a gradual wear out of the tendon(s) of the rotator. Rotator cuff tear symptoms include pain radiating from the shoulder down to the arm, weakness, and, in some cases, complete loss of arm lift ability. An arthrogram is one of the diagnostic tests. This involves injecting radio-opaque dye into the shoulder. If it leaks from the rotator-cuff, it can either be seen on an x-ray or ultrasound. However, an M.R.I. will not be performed. The most commonly used test for diagnosing is the rotator wrist.
The treatment of young and middle-aged patients involves either open or arthroscopic repair of the torn tendon. Activity modification, anti-inflammatory medication and physical therapy are all common for older patients. Cortisone injections, cortisone injections, and activity modification are also options. Patients with severe pain or dysfunction who do not respond to conservative treatment may consider surgery.
TREATMENT
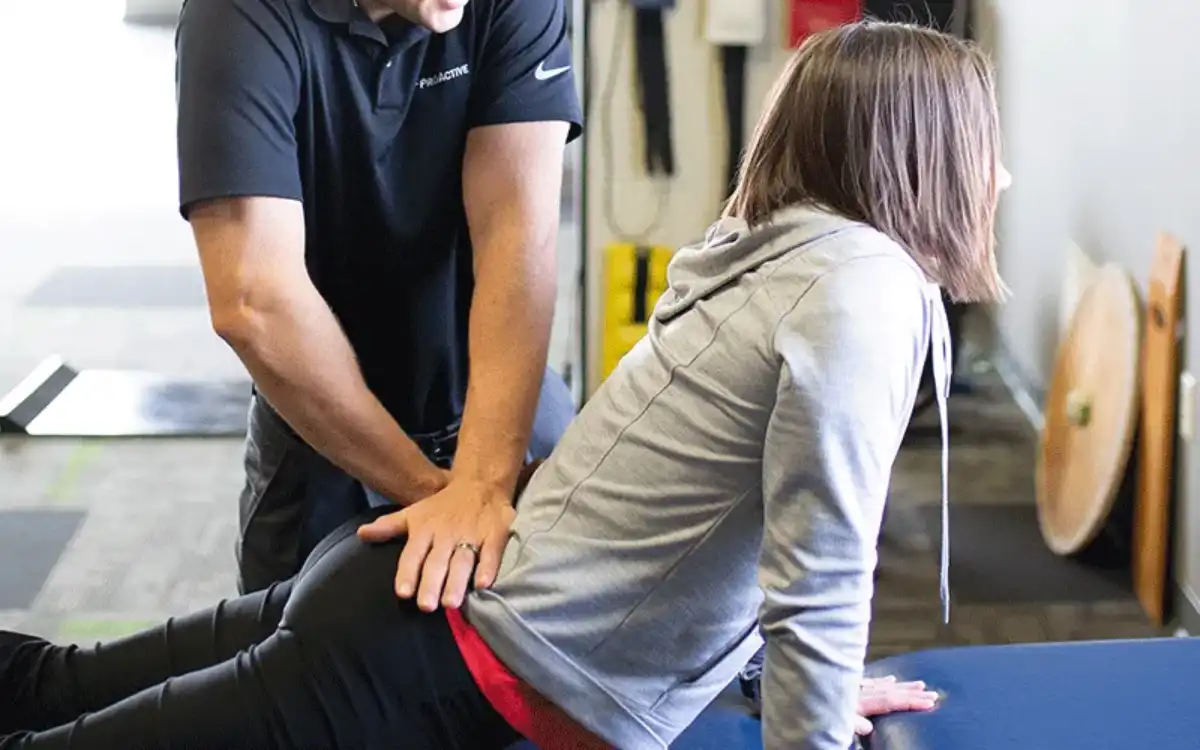
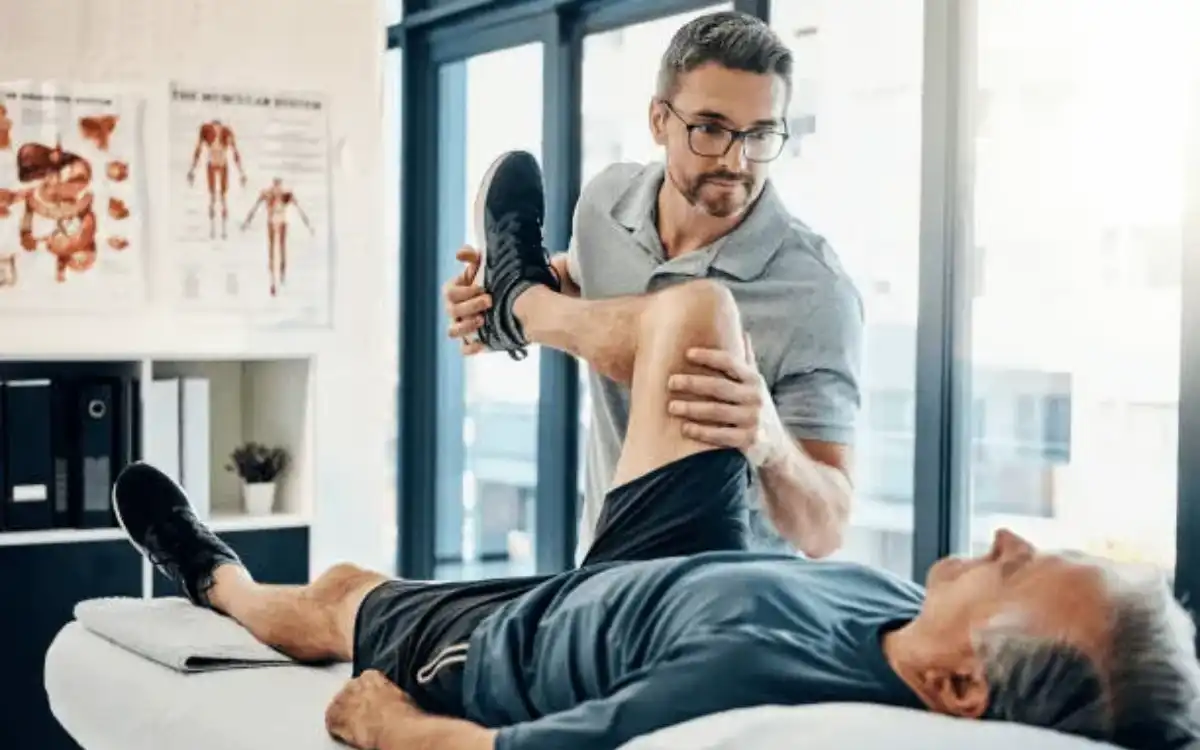
Possible Treatments
- Active Assistive Range of Motion
- Aerobic/Endurance Exercise
- Core Strengthening
- Cryotherapy or Cold Therapy
- Electrotherapeutic Modalities
- Isometric Exercise
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF)
- Proprioception Exercises
- Physical Agents
- Shoulder Active Range of Motion
- Shoulder Joint Mobilization
- Shoulder Passive Range of Motion
- Shoulder Resistive Range of Motion
- Soft Tissue Mobilization
- Stretching/Flexibility Exercise
GOALS
Possible Treatment Goals
- Decrease Risk of Reoccurrence
- Improve Fitness
- Improve Function
- Improve Muscle Strength and Power
- Increase Oxygen to Tissues
- Improve Proprioception
- Improve Range of Motion
- Self-care of Symptoms
- Improve Tolerance for Prolonged Activities
- Improve Wound Healing